FOR RELEASE: August 1, 2023
Survey on Election Readiness: An Analysis of the Dynamics and Perspectives Surrounding the Multi-party System and Local Government Elections in Puntland
Democracy in Flux: A Multifaceted Exploration of Electoral Perspectives in Puntland
FOR INFO OR OTHER INQUIRIES:
Bayan Research Center
3055 Old Highway 8, Sutie #155,
St. Anthony, Minnesota 55418
612-345-7092
Survey on Election Readiness: An Analysis of the Dynamics and Perspectives Surrounding the Multi-party System and Local Government Elections in Puntland – Somalia.
Somalia - Puntland
About Bayan Research Center
Bayan Research Center (BRC) is a non-profit think tank and policy analysis organization with bases in Minnesota, Nairobi, and Mogadishu. Registered in the United States of America, Kenya, and Somalia, our mission is to conduct in-depth research and studies that lead to innovative ideas and visions aimed at addressing the educational, political, economic, religious, and social challenges faced by society at local, national, and global levels.
The Center aims to generate ideas, enlighten public opinion, and inform the public about the global attitudes, issues, and social trends shaping Somalia and the world. We do not take policy positions. Instead, we conduct public opinion polling, demographic research, content analysis, and other data-driven social science research in cooperation with experts, governmental, and non-governmental institutions. All of the Center's reports are available at www.bayanresearch.org. The Bayan Research Center is a nonprofit, tax-exempt 501(c)(3) organization.
Executive Summary
The study aimed to provide a comprehensive analysis of the challenges, dynamics, and implications of the electoral processes in Puntland, focusing on the perspectives, opinions, and experiences of the participants. To pursue these goals, the Bayan Research Center conducted empirical analyses. The data indicated that 72% of the study respondents work in the private sector. Moreover, a significant majority of respondents supported the multi-party electoral system in Puntland, with 89% in favor, while 84% of the interviewees supported the one-person-one-vote system. In addition, 62% of the study's participants endorsed their support if the government proposes a technical extension.
Furthermore, the data revealed that individuals who had attended college and earned bachelor's, master's, or doctorate degrees showed significant support for Puntland's multiparty system. Conversely, young respondents aged 18 to 35 demonstrated substantial support for the one-person- one-vote system, reflecting the aspirations of the youth in Puntland. In contrast, 11% of respondents expressed opposition to the multi-party electoral system, 16% disfavored the one- person-one-vote system, and 38% of respondents strongly opposed the idea of a technical extension, expressing concerns about the extension itself. Similarly, older, and less educated individuals were less likely to support the multi-party system.
The survey also indicated that both significant supporters and critics of the one-person-one-vote system reside in four major cities across Puntland: Bosaso, Garowe, Galkayo, and Qardho. However, the degree of support or opposition differed significantly among these locations.
Introduction
The Puntland State of Somalia was established in 1998 in response to the Somali Civil War that began in 1991. A homegrown constitutional conference took place in Garowe, the capital of Puntland, over the course of three months. This conference was attended by political leaders, traditional elders (Issims), members of the business community, intellectuals, and representatives from civil society. Consequently, the autonomous Puntland State of Somalia was officially established with the aim of providing essential services to the population, ensuring security, promoting trade, and engaging with domestic and international partners. As part of its inception, a plan was introduced to transition to a one-person-one-vote election system, with the first election scheduled to be held within three years, starting from 2001.
The implementation of a one-person-one-vote election system in Puntland marks a significant milestone in the region's democratic journey. Over 25 years since the establishment of the autonomous Puntland State of Somalia, efforts have been made to transition from traditional power-sharing models to a more inclusive and representative electoral process.
The Transitional Puntland Electoral Commission (TPEC) has played a crucial role in overseeing the electoral preparations and facilitating the local council elections. The process began in October 2021 with the launch of elections in three early election districts: Qardho, Eyl, and Ufeyn. This initial phase served as a test run to identify and address any logistical challenges, ensuring a smooth electoral process.
Building on the lessons learned from the early election districts, the electoral commission expanded its efforts and successfully conducted elections in 30 districts in May 2023. This broader participation allowed a larger portion of the population to exercise their right to vote and actively engage in the democratic process. It's important to acknowledge the efforts of all stakeholders involved - political elites, traditional elders, members of the business community, intellectuals, and civil society representatives. Their active participation and collaboration were instrumental in ensuring the smooth conduct of the elections. Their collective commitment to democratic principles and values underpinning the electoral process contributed to the positive outcomes witnessed in Puntland.
However, it's important to note that despite progress in conducting local council elections, certain challenges and limitations were experienced in specific regions. In the Nugaal Region, for instance, three districts—Garowe (the capital city of Puntland), Dangorayo District, and Godob Jiiraan District—did not participate in the local government elections. This non-participation was primarily due to disputes within certain clans that opposed the elections. The existence of these disputes highlights the complex dynamics and competing interests that can emerge during transitional periods towards a fully inclusive electoral system. It underscores the need for ongoing dialogue, reconciliation, and efforts to address underlying grievances to ensure the broadest possible participation in future elections.
The exclusion of these three districts from the electoral process underscores the importance of fostering an environment of trust, inclusivity, and consensus-building among various communities. Addressing the concerns of dissenting clans and working towards reconciliatory measures will be crucial for future electoral processes in these districts and for the overall stability and inclusivity of the democratic system in Puntland.
The Bayan Research Center (BRC) conducted a study to analyze the multi-party system and local government elections in Puntland. The study focused on understanding the perspectives, opinions, and experiences of respondents across different age groups, genders, and educational backgrounds. It aimed to provide a comprehensive analysis of the challenges, dynamics, and implications of the electoral processes in Puntland. The study also examined the level of support for the multi-party system, the government's potential to hold a one-person, one-vote election, and the public's stance on granting a technical extension if proposed by the government.
Sampling
The study used a sample of respondents from various cities and districts in Puntland to ensure a diverse representation. The cities and districts included Bosaso, Burtinle, Badhan, Buuhoodle, Caluula, Carmo, Dhahar, Galdogob, Laasocaanood, Galkayo, Garowe, Qardho, and others. The distribution of participants across these locations allowed for an examination of the multi-party system and local government elections within each locality.
Data Collection
The study employed survey methods to gather data from the participants. Specific details regarding the survey instrument, such as the questionnaire used, the number of questions, and the response format, were not provided in the text.
Election Readiness Survey Analysis
The Bayan Research Center (BRC) conducted a study that focused on the multi-party system in Puntland and the local government elections in the region.
Distribution of respondents by age
The age breakdown of the survey respondents and their distribution is presented below:
The 18-35 age group had the highest number of participants in the survey, which makes 56% of the total survey population. The significant representation of young adults in the study suggests their active involvement and interest in the multipart system and local government elections. The 36-50 cohort had the second highest making 29% of the total sample. This age group brings a combination of youthfulness and experience, offering insights from individuals who have likely witnessed and participated in multiple election cycles. The 51-65 cohort represents 11% of the total survey population. This segment includes individuals with a wealth of life experience and potentially a long history of engagement with the political processes in Puntland. The least was the age group over 65 which constitutes 4% of the total sample. The diverse age distribution of the respondents ensures a comprehensive analysis of the multipart system and local government elections in Puntland.
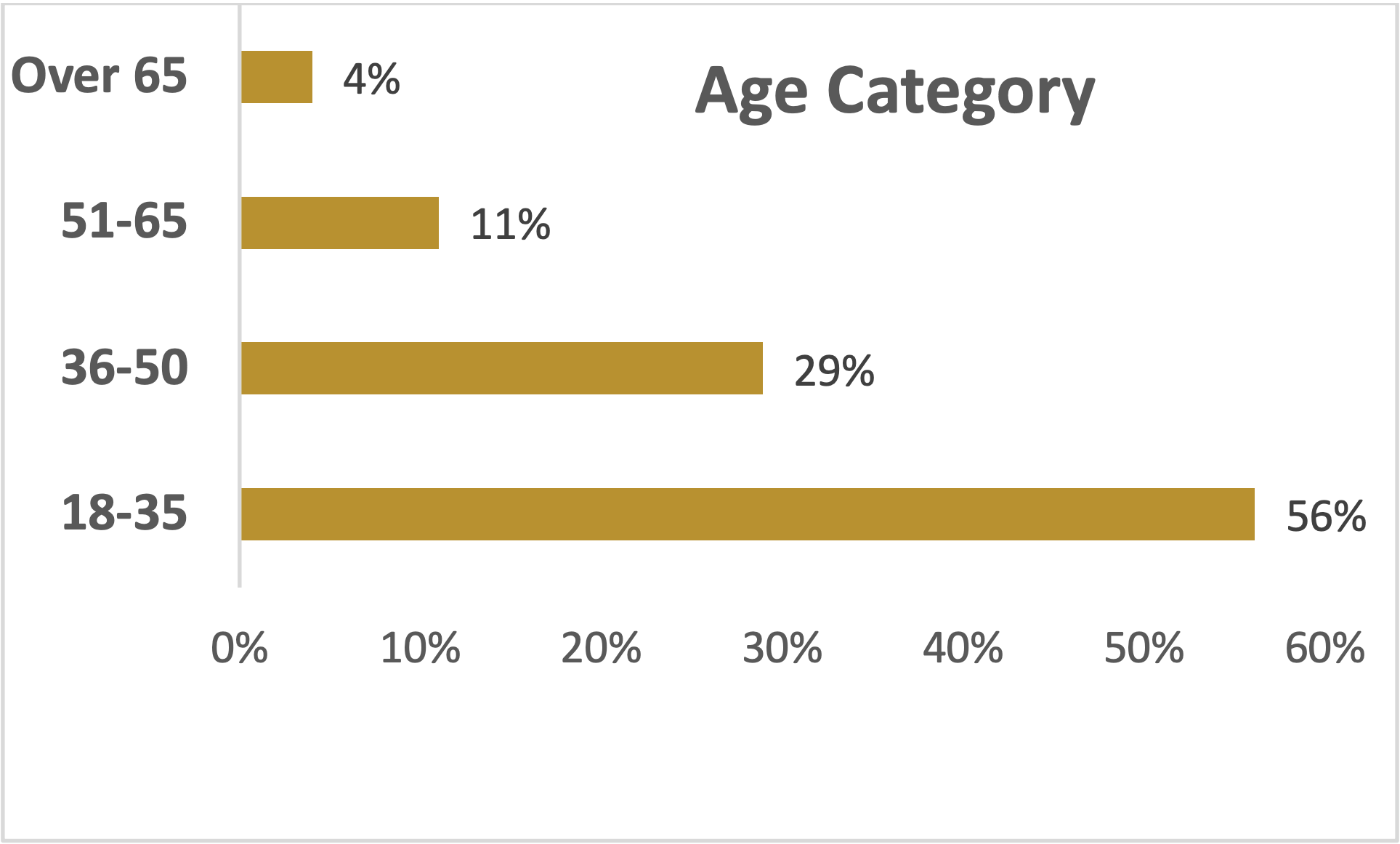
Note: No response answers not shown.
Source: Survey of Puntland adults conducted
May 1 –25, 2023.
BAYAN RESEARCH CENTER
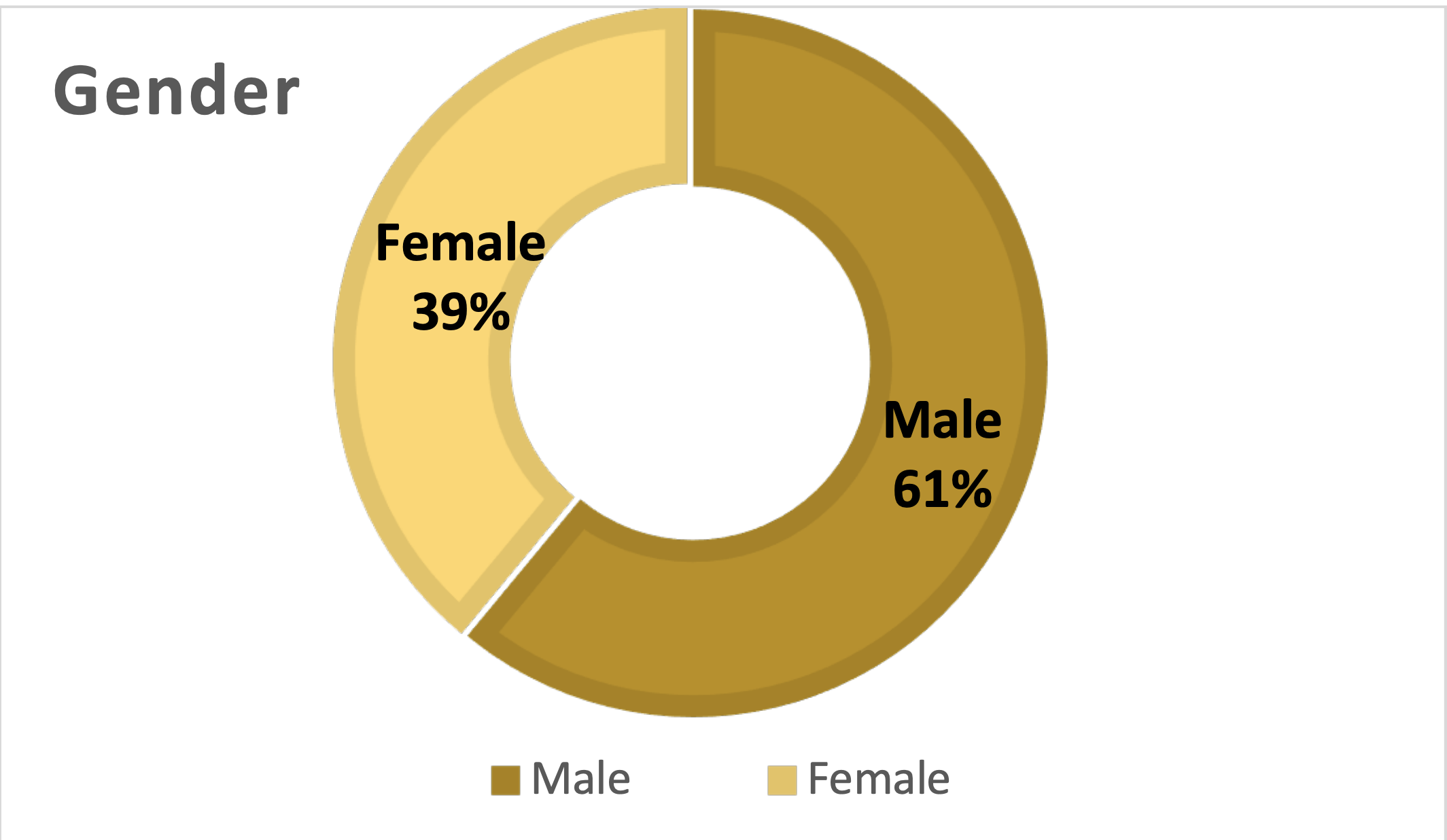
Distribution of respondents by gender
The male respondents make up the majority, comprising of 61% of the total survey sample. The higher representation of males in the study suggests their active participation and interest in the subject matter. The Female respondents accounted 39% of the total respondents. This indicates a strong engagement and participation of women in the study, reflecting their interest and involvement in the multi-party system and local government elections in Puntland. The inclusion of diverse perspectives from females contributes to a comprehensive analysis of gender dynamics and the role of women in the electoral processes. The gender data collected in the study ensures a balanced analysis by including the perspectives of both women and men. The inclusion of perspectives from different age groups allows for a holistic understanding of the challenges, dynamics, and impact of these electoral processes across various generations. The inclusion of female respondents allows for an examination of gender-specific issues, such as representation, participation, and barriers faced by women in the electoral processes.
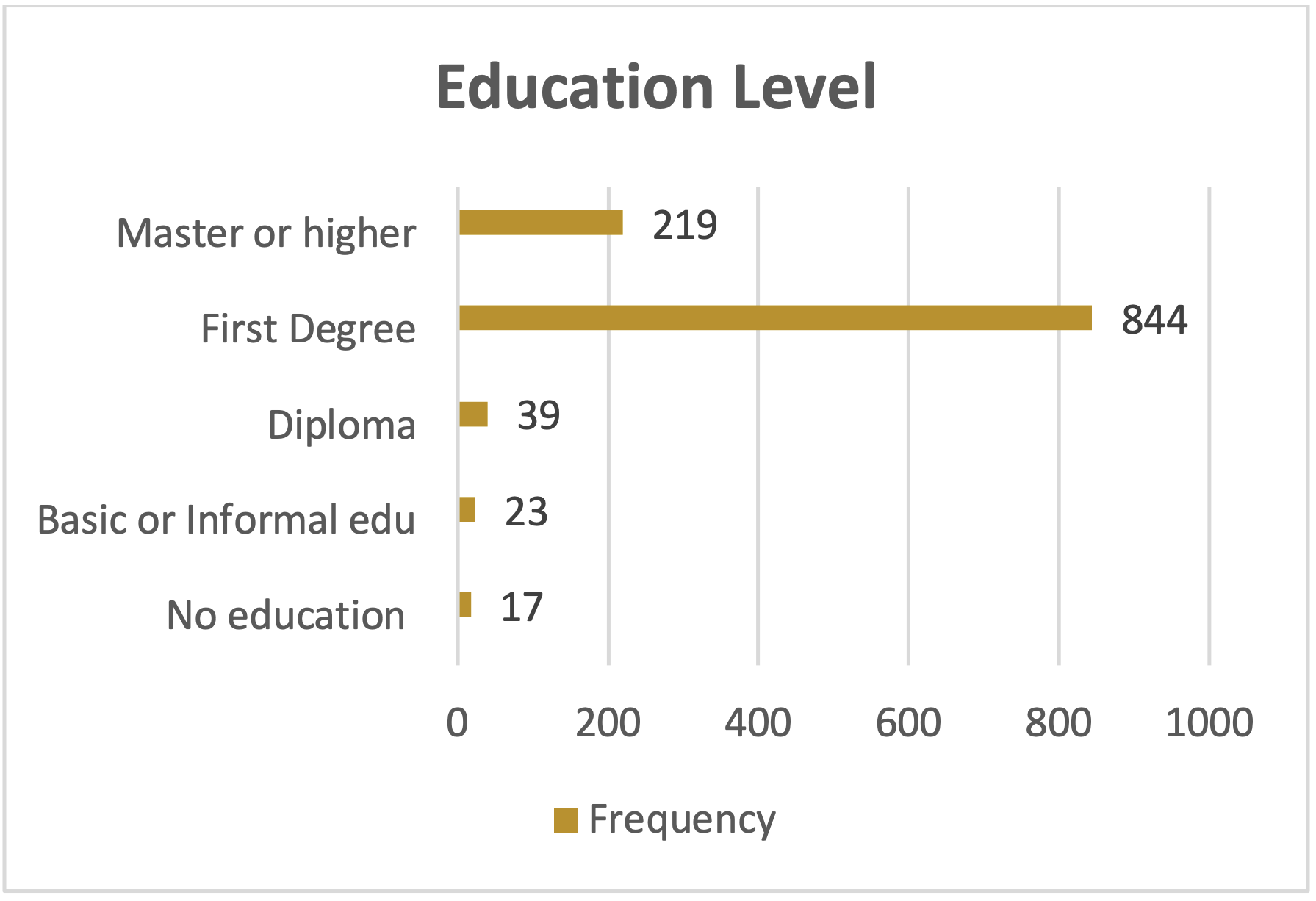
Education level of the respondents
The participants in the study conducted by the Bayan Research Center (BRC) exhibited a wide range of educational backgrounds. The data showed that a significant proportion of 17.3%, of the participants had attended an institute or university, indicating a possession of higher education qualifications. Another 1.1% had basic education, which provided insights from a foundational educational background. Additionally, 3.4% held a diploma, which offered unique perspectives from vocational or technical fields. Moreover, 1.1% possessed a doctorate degree, which contributed to their expertise and research insights. Furthermore, 12.2% had higher education qualifications beyond a bachelor's degree, while 44.5% held a bachelor's degree, representing a substantial proportion with undergraduate education. Only 1.0% had informal education, providing diverse perspectives from non-traditional means. Furthermore, 18.0% had a master's degree, offering deeper insights from advanced studies, and finally, 1.5% had no formal education, which shed light on the experiences of a marginalized segment.
Participants by location
The study analyzed the multiparty system and local government elections in Puntland, focusing on key distributions. Bosaso had the highest number of participants, with 251 respondents, representing 22% of the total sample. Burtinle had 5.1% of the sample, with 58 respondents, providing valuable insights into the elections. Badhan had 3%, Buuhoodle had 2%, Caluula had 2%, Carmo, Dhahar, Galdogob, and Laasocaanood had similar representation, providing valuable perspectives. Galkayo had 194 respondents, representing 17% of the total sample, and Garowe, the capital city, had the second- highest number, accounting for 20%. Meanwhile, Qardho had 137 respondents, accounting for 12% of the total sample while other cities/districts had 5%, with 57 participants.

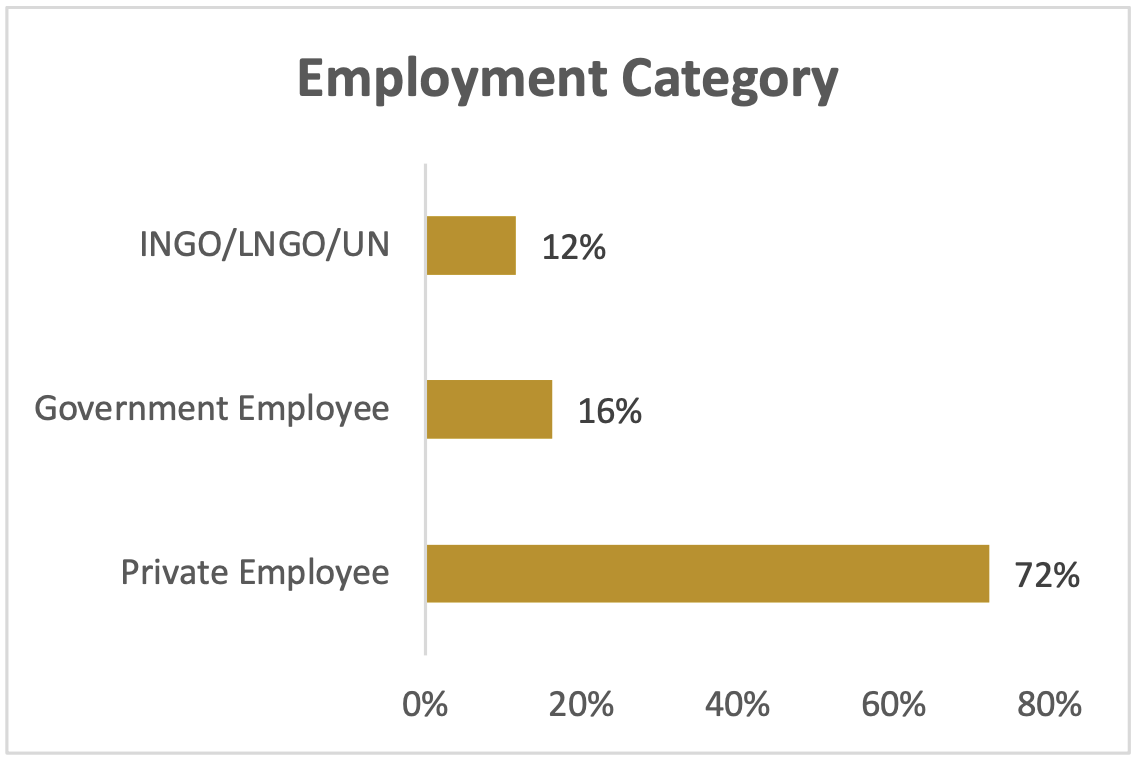
Distribution of respondents by occupation
The study revealed that Private employees, including businessmen and women, provided valuable insights into their views on the multi-party system and local government elections accounting 72% of participants followed by government employee 16% and lastly 12% of the participants were employees of institutions such as non- governmental organizations (NGOs), international non-governmental organizations (INGOs), or the United Nations (UN). These individuals provided valuable insights into their perspectives on the multi- party system and local government elections.
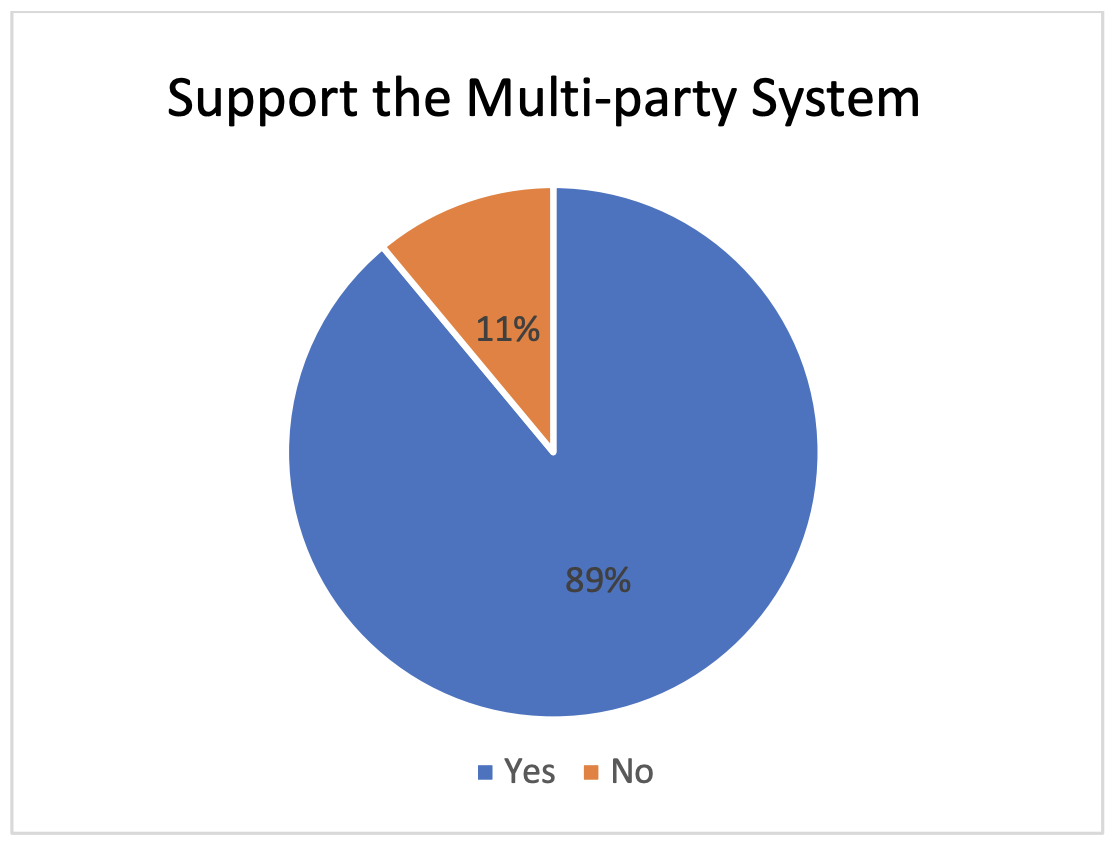
Supporting Multi-Party Electoral System in Puntland
The study revealed that 89% of respondents supported the multi-party electoral system in Puntland, indicating a strong endorsement of its value for democratic governance and political representation. This support reflects a desire for a robust and inclusive political landscape. However, 11% of respondents who expressed opposition likely have concerns or reservations about the system's implementation or impact on governance and stability. Understanding the reasons behind their dissent can provide valuable insights for policymakers and stakeholders in Puntland to address and engage with their concerns constructively. Overall, the study highlights the importance of strengthening democratic processes, ensuring fair elections, and addressing challenges or criticisms raised by the minority.
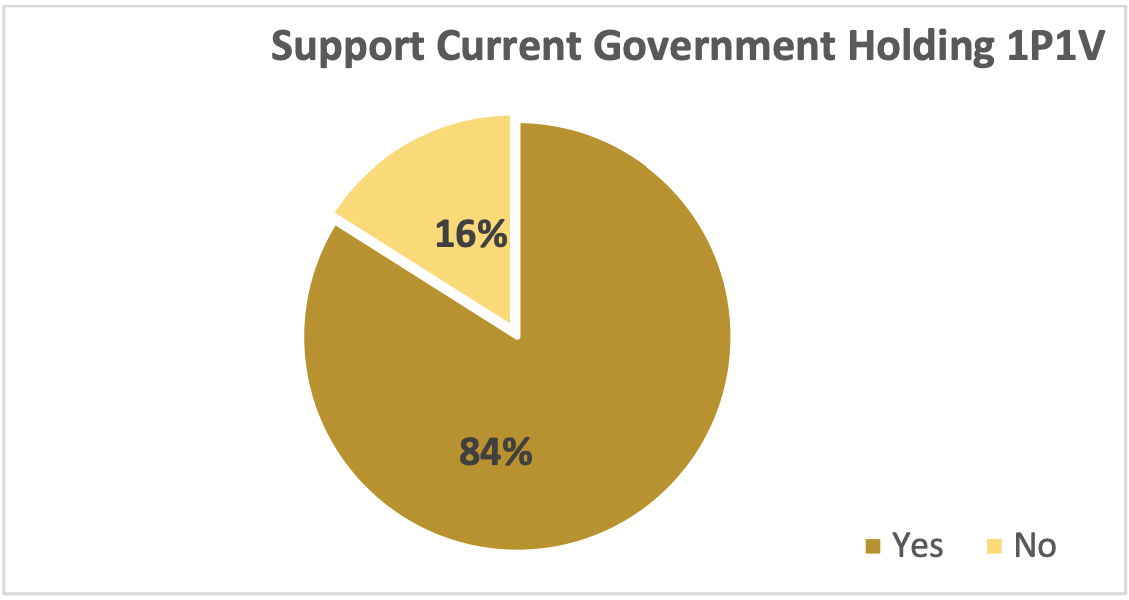
Would you support the current government holding a one person, one-vote election?
The Bayan Research Center's study on respondents' perspectives on supporting a one-person, one-vote election in Puntland found a significant support of 84%, while 16% expressed opposition. The study addresses the political landscape and government role in conducting elections, particularly the Transitional Puntland Electoral Commission (TPEC).
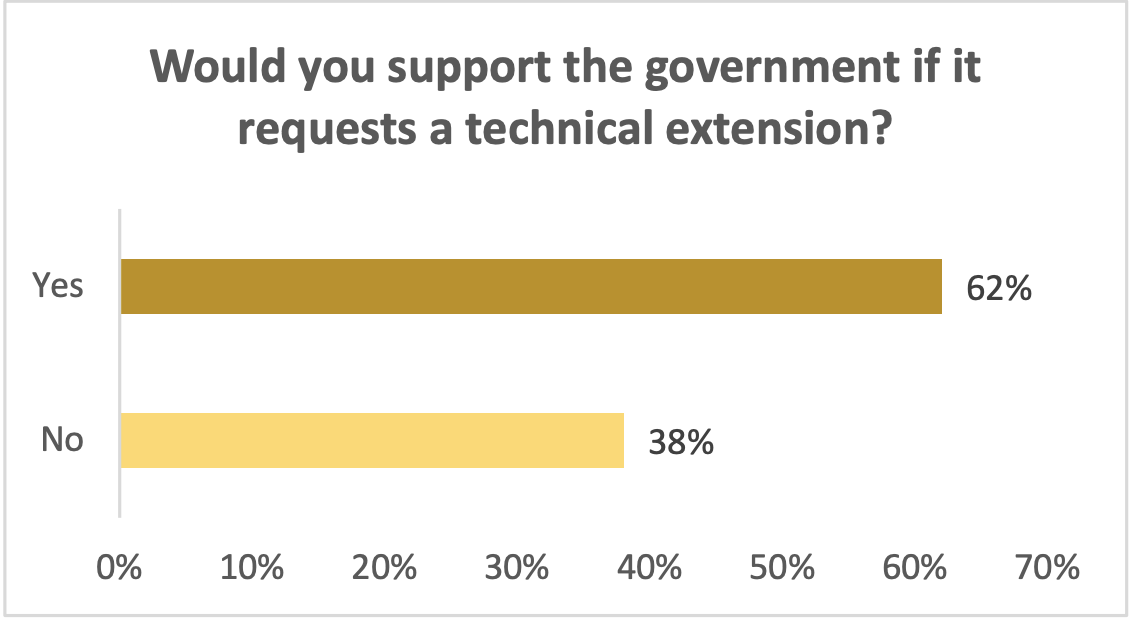
Would you support the government if it requests a technical extension?
As illustrated in the bar chart, 62% of the study's participants would endorse a government proposal for a technical extension, suggesting a majority of respondents in the study would support such a measure. Conversely, 38% of respondents strongly opposed the idea, expressing concerns about both the extension and the proposed multi-party election system.
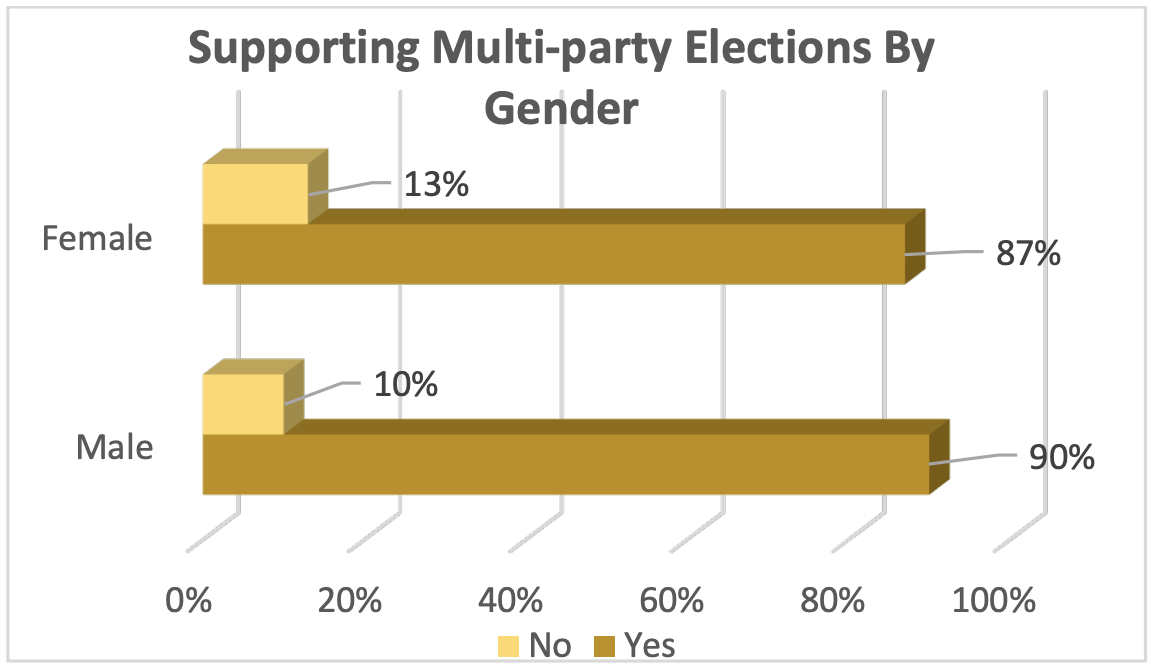
Distribution of Supporting 1P1V System among Genders
Findings of the study indicated that both males and females strongly supported multiparty elections in Puntland. 87% of female participants supported IPIV system while only 13% of female participants unfavored IPIV system. Similarly, 90% of male participants favored IPIV whereas only 10% not supported the multiparty election system.
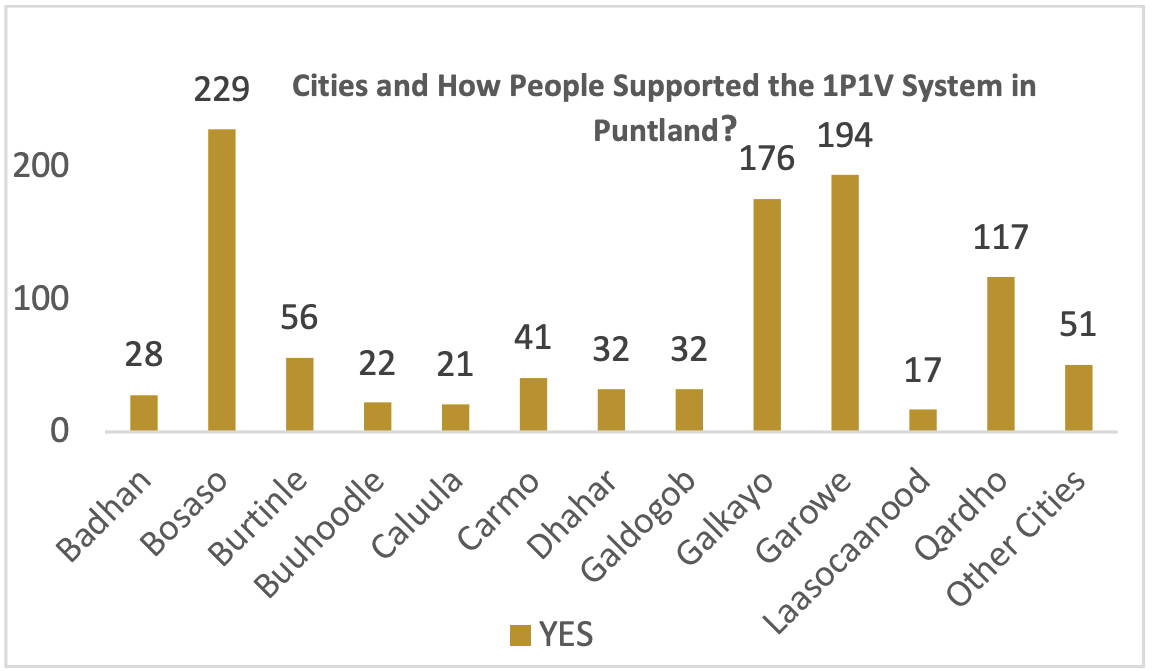
Cities and How People Supported the 1P1V System in Puntland
According to the data presented in the right- side bar chart, residents of Bosaso exhibit the highest level of support for the IPIV system, with Garowe, Galkayo, and Qardho following in descending order. Conversely, out of the 126 individuals who expressed a lack of favor towards the IPIV system, 34 respondents were from the capital city of Garowe, with Bosaso, Qardho, and Galkayo following suit. This observation highlights the fact that a majority of the study participants reside in the major cities of Puntland, emphasizing the significance of their perspectives in shaping the understanding of the IPIV system.
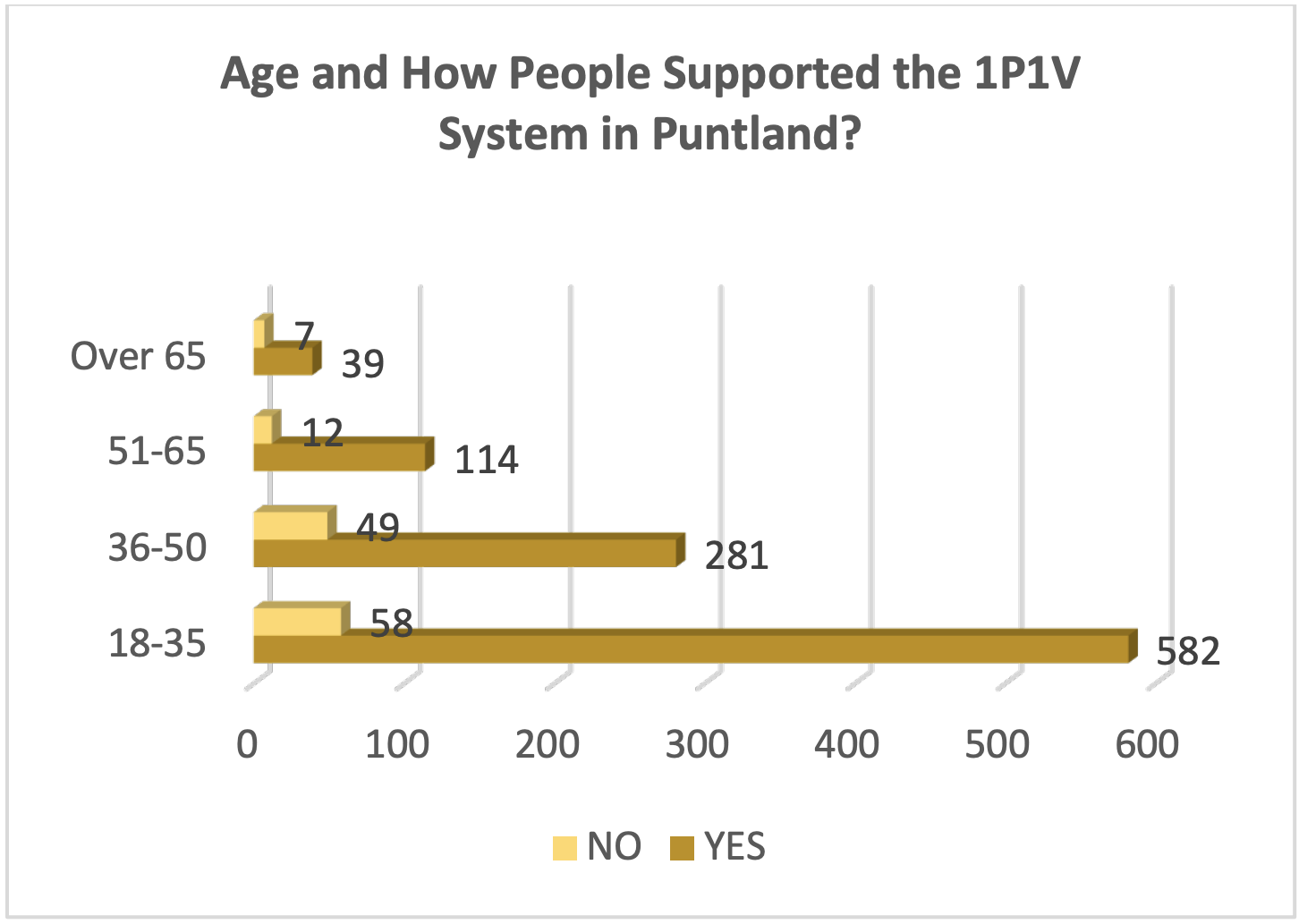
Age and How People Supported the 1P1V System in Puntland
The survey results indicate that young respondents aged 18 to 35 demonstrate significant support for the IPIV system, reflecting the aspirations of the youth in Puntland. Conversely, the older demographic displayed less enthusiasm towards the IPIV system.
Recommendations
The policy implications that emerged from this survey, as well as the institute's recommendations, are as follows:
- The people of Puntland aspire to and eagerly anticipate a one-person-one-vote system and a multi-party system in order to exercise their electoral rights, live under a unique democratic experiment, and celebrate the twenty-fifth founding anniversary of their nation.
- The 2023 Puntland elections indicate that 342,216 people registered and received their IDs to vote, of which 215,035 people cast their votes. If the government had formulated better strategies and invested more in public awareness and education, the number of participants could potentially have doubled.
- As Puntland transitions to a multi-party system, raising societal awareness about political participation is particularly crucial. It facilitates a smoother transition, promotes informed decision-making, encourages active citizenship, ensures fair representation, fosters accountability, cultivates democratic values, and builds awareness against deliberate misinformation. All of these contribute to promoting political stability in Puntland.
- There should be a stronger focus on dialogue, reconciliation, and conflict resolution to mitigate disputes and enhance stability during transitional periods.
- It is important to enhance the inclusivity and accessibility of the multi-party system and local government elections by considering the perspectives and needs of diverse age groups. This includes taking measures to increase the participation and engagement of women, youth, and individuals experienced in the multi-party system and local government elections.
- Continuous engagement with stakeholders, including political elites, traditional elders, members of the business community, intellectuals, and civil society representatives, is necessary to maintain their active participation and collaboration in Puntland's democratic processes.
- The peaceful transition of power and preservation of the term of rule (every 5 years starting from January 8, Puntland's election day) are fundamental pillars for building societal trust and are key to resolving disputes peacefully.
- However, if the transition to a multi-party system and a one-person-one-vote system necessitates a technical extension of the term of rule, the government is responsible for enlightening and guiding the public. This includes developing a roadmap for this process, involving stakeholders, and achieving national consensus in a timely manner, all before the approach of election dates. These steps are essential to prevent a civil war and to achieve national desired goals.
- Given that the Puntland government is going through a critical and sensitive transitional period, the Bayan Research Center advises that any parliamentary reforms or constitutional amendments need approval from the Supreme Court. Furthermore, these changes should require a national meeting that brings together representatives from various political, social, and cultural interests to discuss and clarify the proposed changes and to achieve national consensus.
Methodology of the Study:
The study titled "Survey on Election Readiness: Analyzing the Dynamics and Perspectives of the Multi-party System and Local Government Elections in Puntland" conducted by the Bayan Research Center (BRC) employed a comprehensive methodology to analyze the multi-party system and local government elections in Puntland. The methodology involved gathering data from respondents across different age groups, genders, and educational backgrounds. The study aimed to provide a comprehensive analysis of the challenges, dynamics, and implications of the electoral processes in Puntland, focusing on the perspectives, opinions, and experiences of the participants.
Survey conducted May 1-25, 2023.
The survey was conducted from May 1 to May 25, 2023, and the analysis in this report is based on online and telephone interviews conducted during this period among a sample of 1,142 adults aged 18 years or older, residing in Puntland State of Somalia. Among the respondents, 210 were interviewed on a cell phone, and 932 were interviewed online.
Reported margins of error, unweighted sample sizes, and statistical tests of significance were adjusted to account for the effect of survey design to ensure a 95% confidence level in the survey results.
Bayan Research Center is a nonprofit, tax-exempt 501(c)(3) organization.
Acknowledgments
This report is a collaborative effort that relies on the input and analysis of a group of talented researchers and creative designers. We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the following individuals:
Research Team
- Tarabi Jama
- Abdifatah Yasin
- Mohamud Ahmed
- Bukhari Abdiwahab
- Abdullahi Osman
- Abdullahi Ali
- Adam Badiic
- Anwar Abdihalim
- Mustafa Shuayb
Digital Producer and Web Publishing
- HabibaLadan Abdi
Communications and Editorial
- Hassan hade
- Said Adam
- Nuruldin Nur
- Mohamed Shuayb
Bayan Research Center gratefully acknowledges the support of diverse groups, companies, individuals, and endorsements from the community. Your continuous contributions have enabled the success of our Center and have allowed us to offer a wide range of services at both local and global levels. Your donations help us advance our Center and facilitate the implementation of highly anticipated programs.
Our annual financial report can be found online. The findings, interpretations, and conclusions in this report are solely those of the author(s) and are not influenced by any donor.
Bayan Research Center
3055 Old Highway 8, Sutie #155,
St. Anthony, Minnesota 55418
612-345-7092
